Peter Thiel’s dream of a libertarian utopia in the middle of the ocean may have finally sunk.
Radio New Zealand is reporting that the French Polynesian government has not renewed its agreement to help the Seasteading Institute, a group created in Silicon Valley, build a permanent and politically autonomous settlement off the coast of the South Pacific islands.
In 2008, Thiel, a billionaire investor and Trump transition team member, launched a mission to develop a floating city, called a seastead, that would operate independently from existing nations. Thiel invested $1.7 million in The Seasteading Institute, but resigned from its board in 2011. He later said in an interview that engineering seasteads is “not quite feasible.”
Here’s what we know about the Seasteading Institute’s plans for a floating city in the South Pacific – and why the deal went under.
Leanna Garfield contributed reporting to this article.
In a 2009 essay, Thiel wrote, "Between cyberspace and outer space lies the possibility of settling the oceans."

Source: Cato Unbound
He imagined "an escape from politics in all its forms" in a new libertarian society.

The PayPal cofounder partnered with Patri Friedman, a Google software engineer who reportedly came up with the idea of seasteads at Burning Man, to launch the institute.

After the group's founding in 2008, some people in Silicon Valley chastised the idea, saying the island paradises would be too wild, expensive, and elitist to generate real results.

But the seasteading concept began gathering support from libertarians and people living outside the Silicon Valley bubble. A 2013 crowdfunding campaign raised over $27,000.

Source: Indiegogo
For years, the Seasteading Institute wanted to set up camp in international waters without any connection to an existing nation. But the group determined the costs were too high.

The United Nations grants every member-state economic and environmental control from its shoreline to 200 nautical miles out. The institute would have to build at least that distance away. Such isolation raises the cost of operations and transportation to get people on and off the seastead.
The institute figured it would cost at least $225 million to build the seastead and another $8 million annually to keep it running. The seasteaders looked to team up with a host nation.

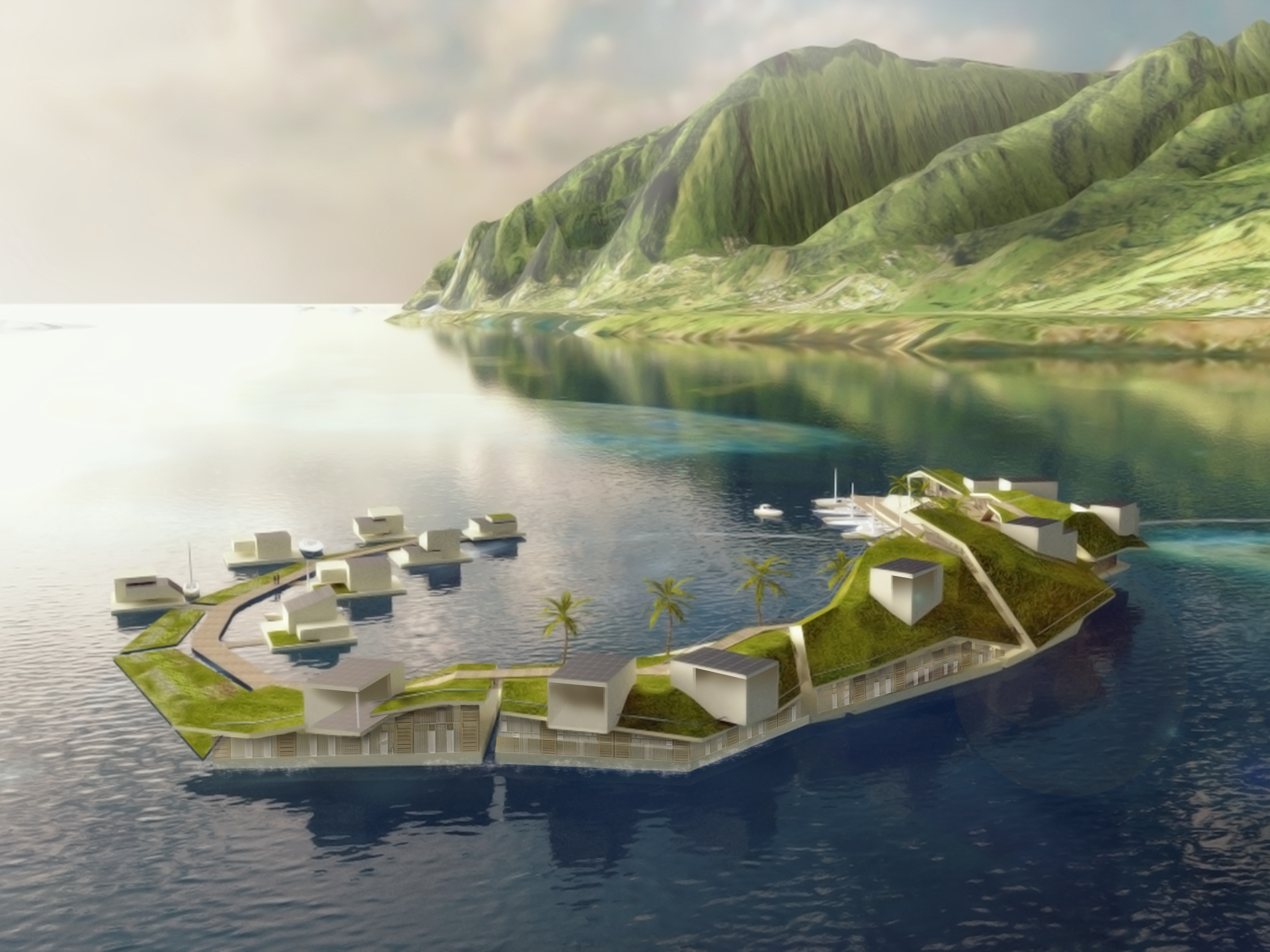
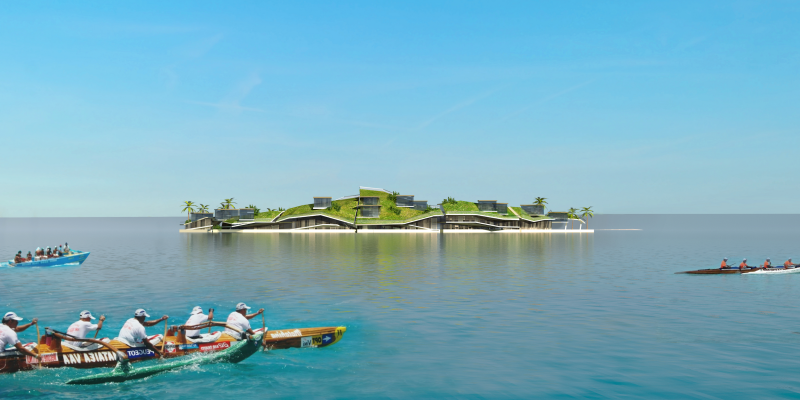
French Polynesia fit the bill.

The island chain is located an eight-hour flight from Los Angeles. It has a fiber cable that runs underwater to Hawaii, providing the bandwidth that tech workers would require.
Rising sea levels threaten French Polynesia's existence, which made a proposal to build new land appealing to the government.

In 2016, the Seasteading Institute sent members to meet with French Polynesian officials. They created a document that would seal the government's intent to work with the group.

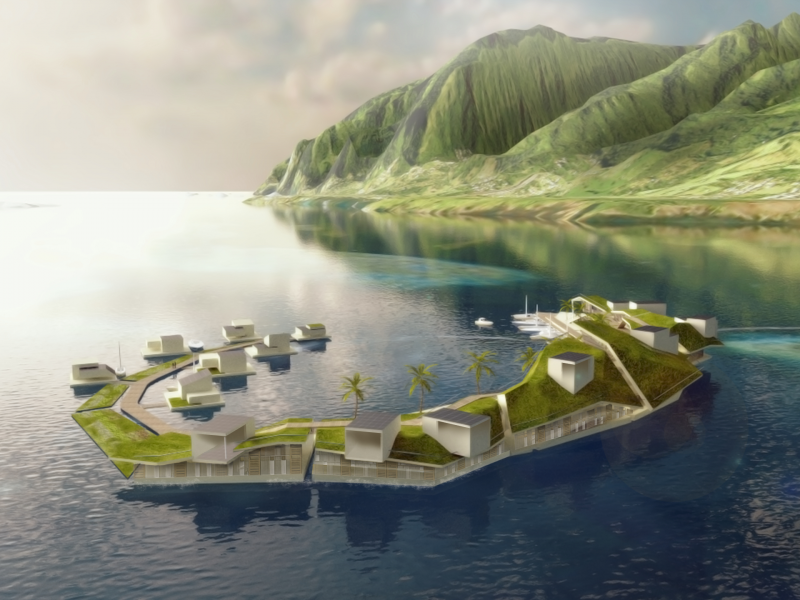
Randolph Hencken, executive director of the Seasteading Institute, told Business Insider shortly after the trip that the floating city would be a small but self-sufficient island.

Source: Business Insider
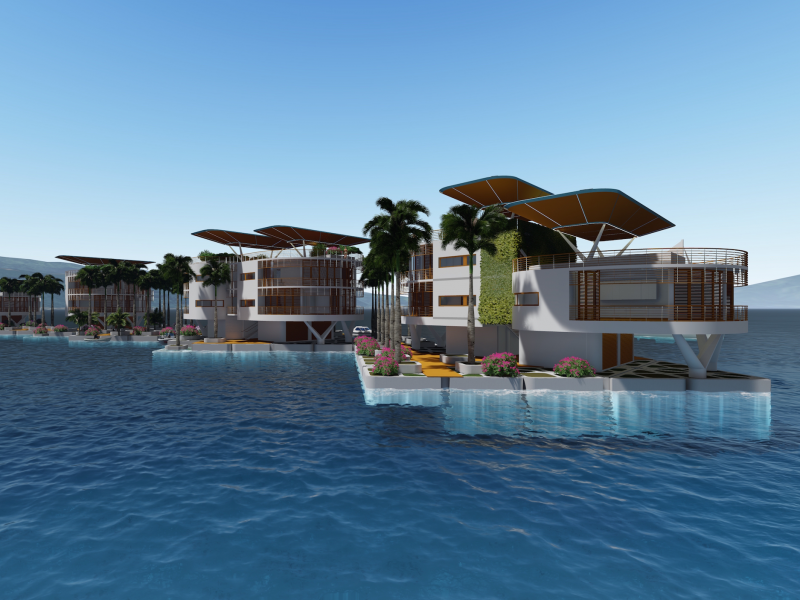
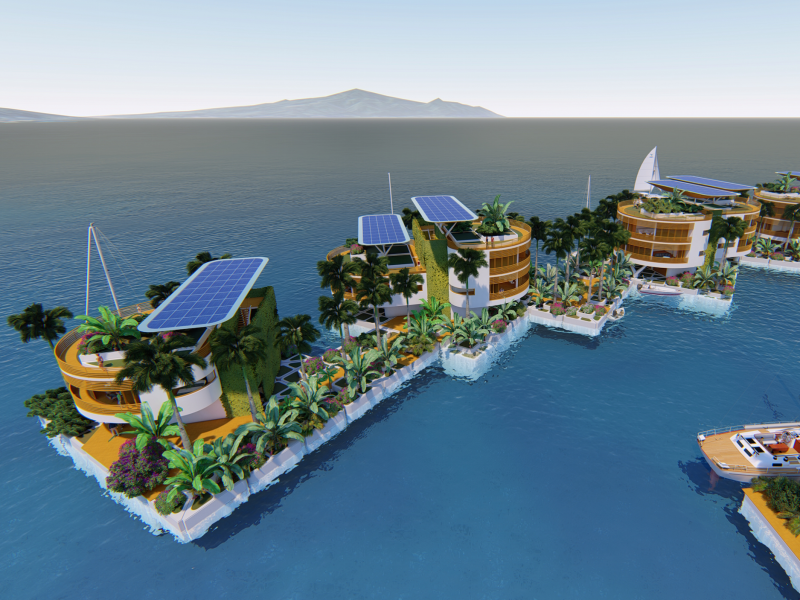
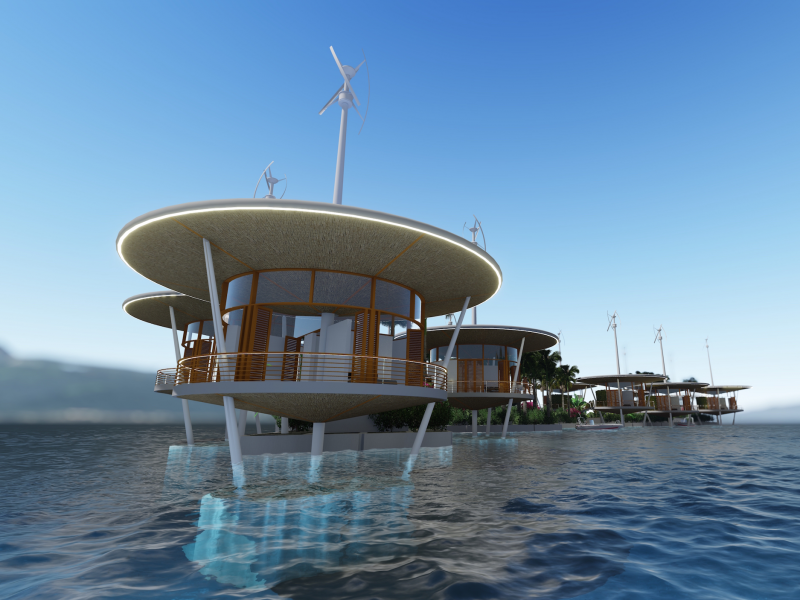
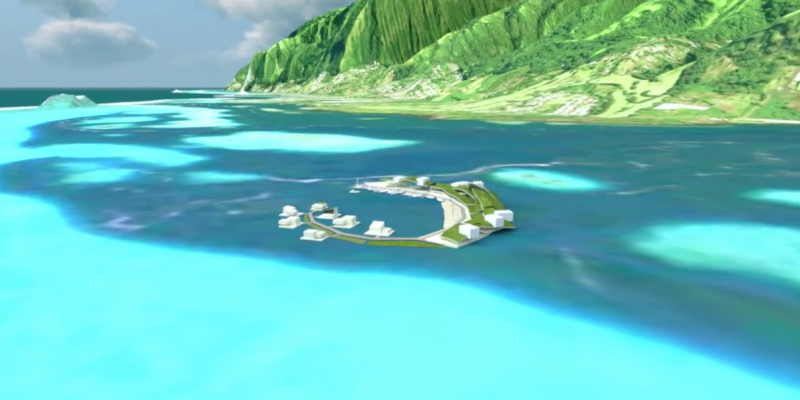
The Seasteading Institute proposed two designs. The first had clusters of floating platforms that featured large solar panels and wind turbines. The second was horseshoe-shaped.
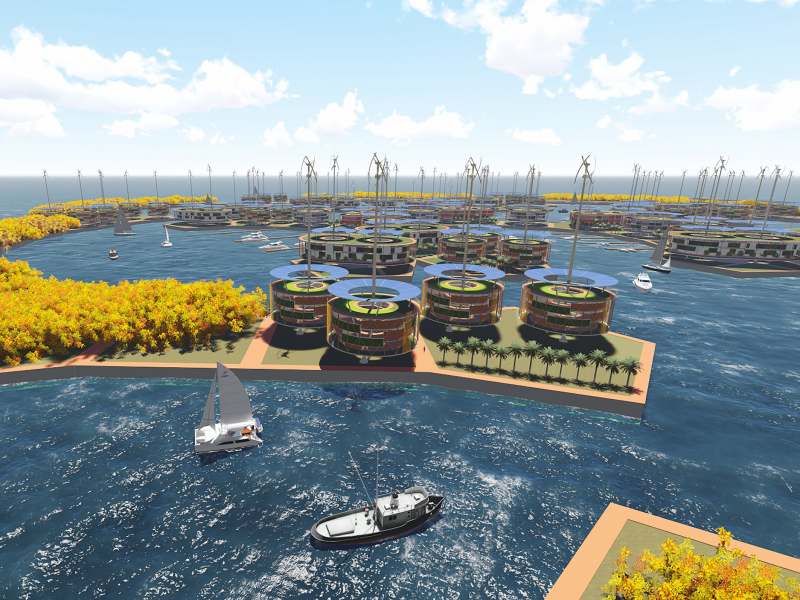

These platforms would house approximately 250 people about a half-mile from the shore.
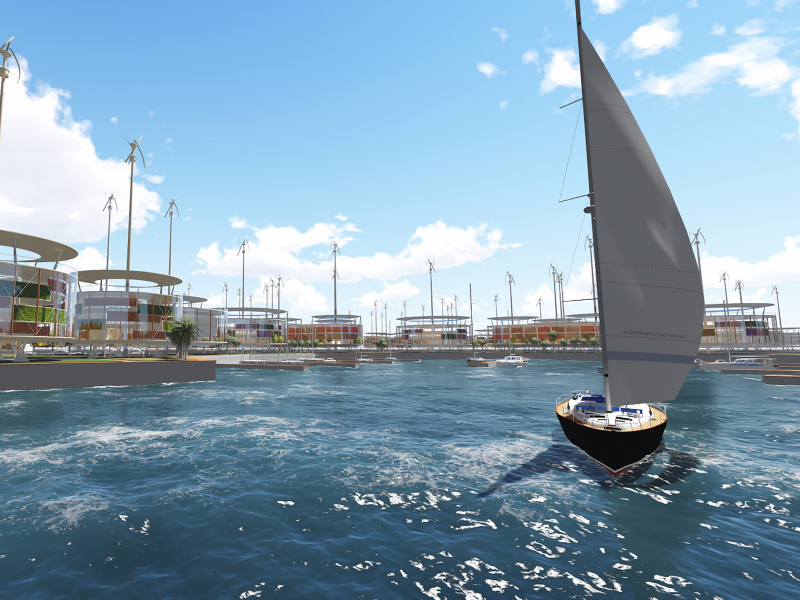

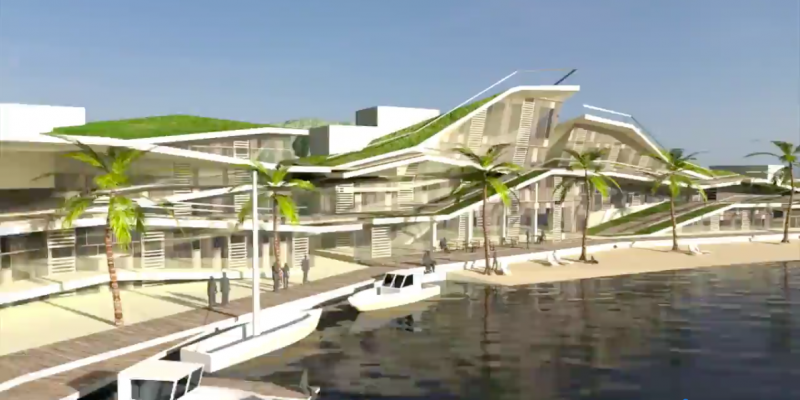
Residents would shop for food, attend school, and go to work on the seastead. They could catch a ferry to the neighboring French Polynesian islands for more substantial errands.
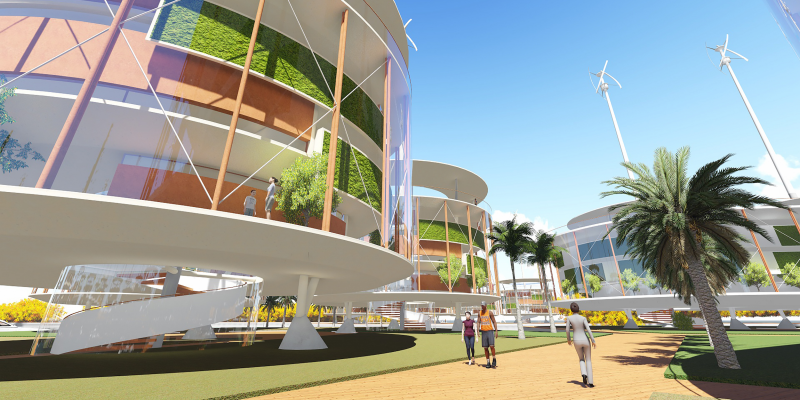

Hencken said that French Polynesia would not govern or tax the libertarian seastead, but residents would abide by some local laws mostly related to crime and the environment.
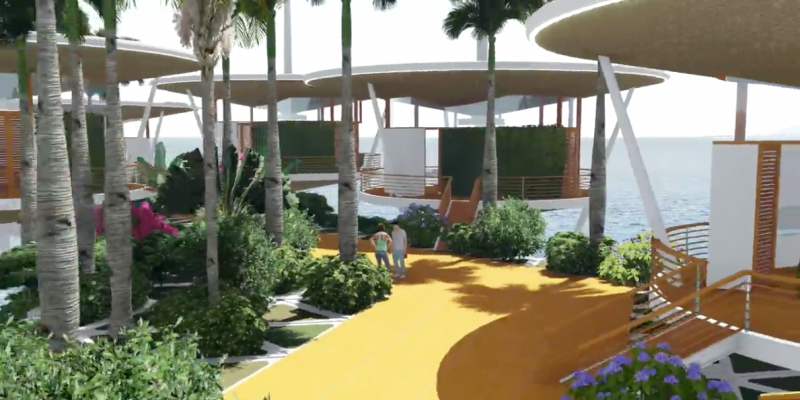

The original goal was to make the housing platforms modular, so if a person grew tired of life on the seastead, they could detach their home and sail away, according to Hencken.
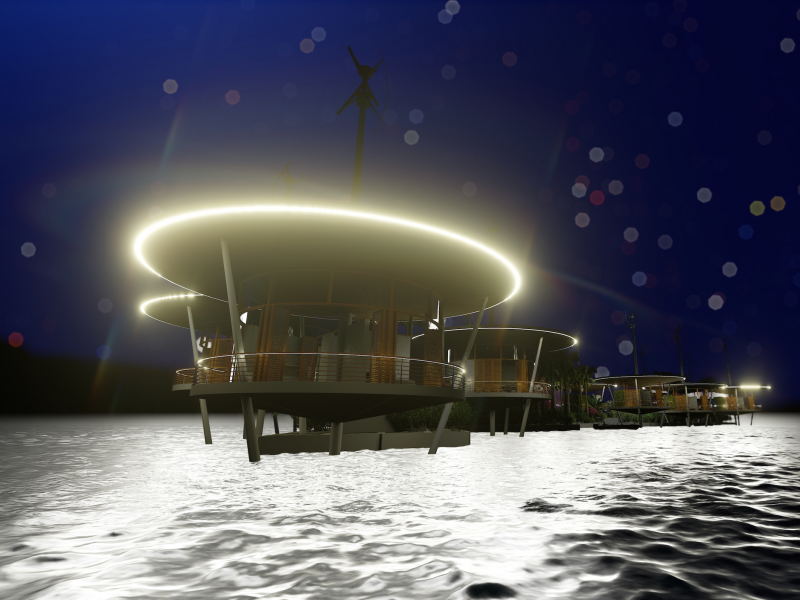

Solar power and recycled ocean water would make the seastead environmentally friendly.
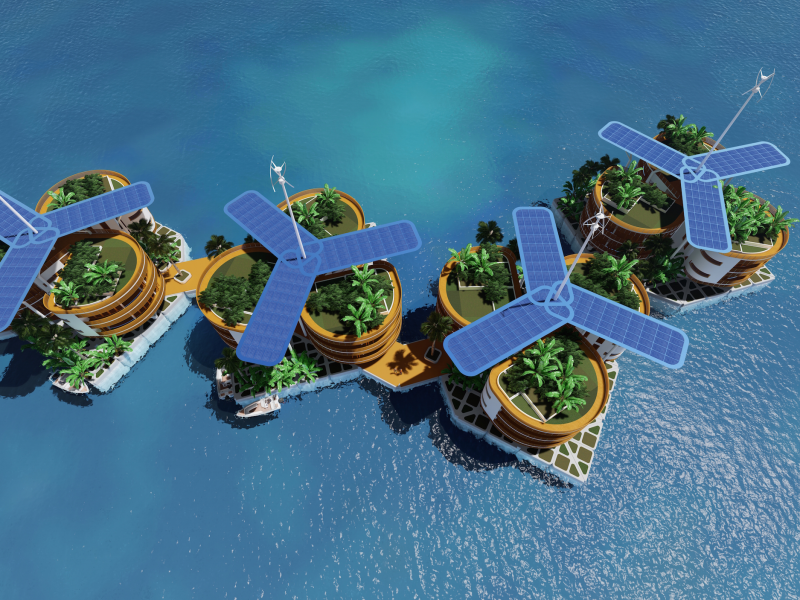

While French Polynesia would provide space for building the project, the institute would cover the costs of construction. It planned to raise money from a handful of investors (who Hencken declined to name), future residents, and supporters from the maritime industry.

In 2016, Hencken said the starting cost of construction would be about $30 million, though that number was subject to change. Each additional platform would cost $15 million more.
As the Seasteading Institute plotted its vision, the locals from Tahiti — the largest island in French Polynesia — grew increasingly concerned about the prospect of "tech colonialism."

A documentary film crew followed the Seasteading Institute leadership at a conference in Tahiti last year. They found that locals weren't given much of a voice at these events.

You can watch the full documentary, "The Seasteaders," by Jacob Hurwitz-Goodman and Daniel Keller, on dis.art.
Alexandre Taliercio, a local radio and TV personality, became one of the most prominent voices of the opposition. During one program, he described the seastead as a cross between "visionary genius" and "megalomania" — an obsession with the domination of others.

Source: The Guardian
In a 2017 interview with The Guardian, Taliercio argued that rich Americans simply want to skip out on paying taxes. "These millionaires have much more to gain than we do," he said.

Locals continued to resist the seastead in public hearings with French Polynesia President Edouard Fritch. In February, the government said its agreement with the Seasteading Institute expired at the end of 2017. It will not pursue a settlement off the coast of Tahiti.

Source: Radio New Zealand
The Tapura Huiraatira party said in a Facebook note that the agreement was intended to create a dialogue between the government, locals, and the Seasteading Institute.
"It's not a contract," the note said. "This document does not bind the country in any way."
It continued, "We are in 2018," and the document "has become obsolete."
The Seasteading Institute has not publicly addressed the sunken plans. Its website features a video about the French Polynesian "floating island" splashed across the front page.
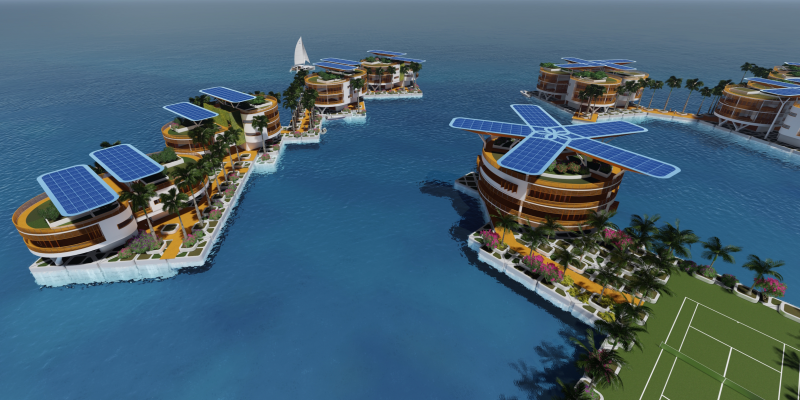

Source: Seasteading Institute
Business Insider contacted the Seasteading Insitute and did not immediately receive comment.
One thing's certain: Peter Thiel isn't moving to a seastead anytime soon.


