- The 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster resulted in widespread contamination throughout Europe.
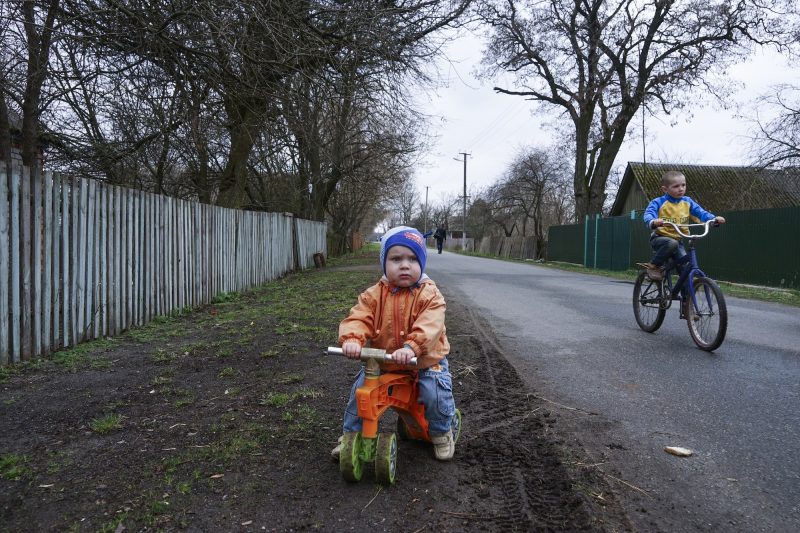
- Today, its legacy still lingers in the radioactive soil and water in Belarus, Ukraine, and Western Russia.
- Children living in these areas have seen health problems such as enlarged thyroids, cancer, and respiratory illnesses, which environmentalists and pediatricians have linked to contaminated food and drink.
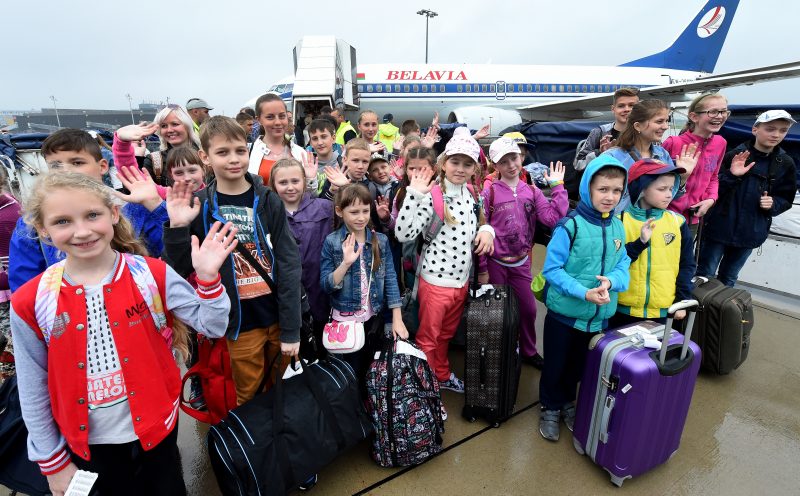
- Each summer, charity organizations offer these kids a chance to vacation in a “clean” city or town, which has both psychological and health benefits.
- But host families are limited, meaning the charities can’t accommodate every child living in a contaminated zone.
- Visit Business Insider’s homepage for more.
Europe is still reeling from the radioactive legacy of Chernobyl, a 1986 nuclear disaster that resulted in widespread contamination in Belarus, Ukraine, and Western Russia.
More than 30 years after the core of a nuclear reactor opened at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, locals near the plant are still exposed to radioactive contaminants through their food and water supply. In 2018, scientists discovered that milk in Ukrainian villages contained five times the amount of cesium considered safe for adults and 12 times the safe limit for children.
Read more: 11 strange events that happened after the Chernobyl nuclear-power-plant accident
As second-generation victims of Chernobyl, children growing up near the disaster zone have seen health problems since birth such as enlarged thyroids, cancer, and respiratory illnesses. Some environmentalists and pediatricians have linked these health problems to contaminated food and drink.
In 1991, Adi Roche, then a volunteer in the Chernobyl zone, received a fax from Belarusian and Ukrainian doctors, asking her to remove children from the area so their bodies could have time to recover from radiation exposure. The fax inspired Roche to found Chernobyl Children International, an organization that sets up vacations in Ireland for children living in contaminated areas. To date, the group has helped organize stays for around 25,000 children, though it estimates that around 1 million children live in zones affected by the disaster.

In the years since, more organizations have pitched in to offer similar vacations.
In 2008, a program called "Blue Summer" began organizing summer stays in Portugal for Ukranian children. The group paid for transportation and health insurance, while host families covered living expenses.
In Raleigh, North Carolina, a charity called Overflowing Hands hosts children ages 6 to 16 for a month and a half over the summer. The charity also pays for pediatrician appointments and dental care.
In the UK, multiple organizations - including the Chernobyl Children's Project, Friends of Chernobyl's Children, and Chernobyl Children's Lifeline - welcome kids for "recuperative" holidays. Some of these children are sick with cancer, while others haven't shown any signs of adverse health effects.

While on vacation, children can develop healthier immune systems and lower their levels of radiation. A chairwoman from the Children's Lifeline recently told the BBC that, after a three-week period of recovery in Scotland, "it takes up to two years for the radiation to build back up again."
There are also psychological benefits to staying where the Chernobyl tragedy is out of sight. A 2005 UN report determined that mental health issues "pose a far greater threat to local communities than does radiation exposure." Children living in contaminated zones may suffer anxiety about becoming ill or having their lives cut short.
But the number of families willing to host these children is limited.
Both the Chernobyl Children's Project and the Chernobyl Children's Lifeline recently told the BBC they had seen a decline in host families in recent years. This year, the Children's Project said they could only host 600 children compared to 3,500 each year in the early 2000s.
There's hope that things could could change following the release of the HBO's "Chernobyl" miniseries in May. The same UK charity groups that worried about a decline in host families told the BBC that the show prompted renewed interest from donors and volunteers.
Read more Chernobyl coverage:
Parts of the Marshall Islands are now more radioactive than Chernobyl because of US nuclear tests
Real-life characters in HBO's 'Chernobyl' on the moment they found out about the disaster