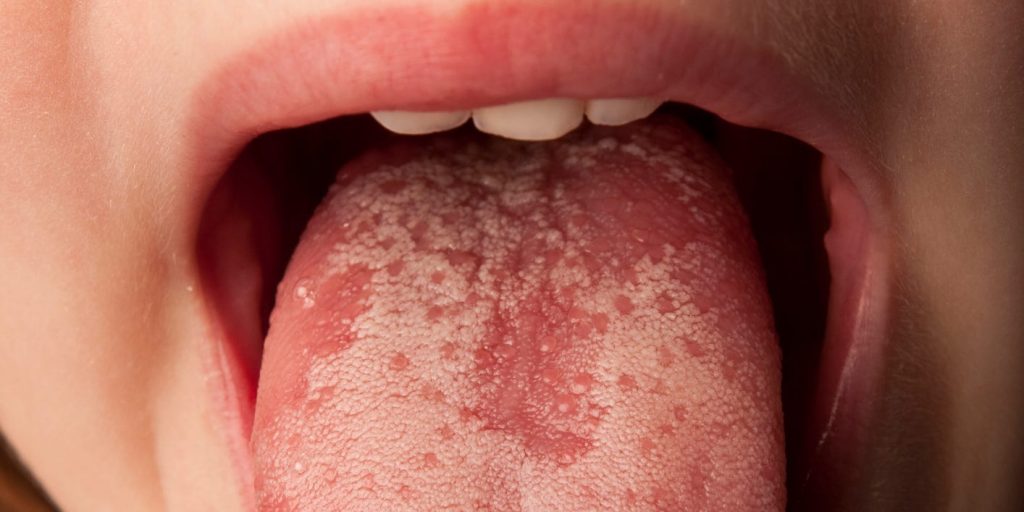
- White spots on the tongue may be callous-like spots that come from biting down.
- White spots can also occur if you have an infection like candidiasis or HPV.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is a type of cancer found on the tongue and may cause white spots.
Have you noticed that your tongue isn't as uniformly pink as it usually is? If you're experiencing white spots or patches on your tongue, you may be wondering what's going on, particularly if you're having any type of discomfort or pain.
White spots on the tongue are common since there are various causes for them. Whether you're experiencing one spot or many, the cause can range from something minor like injury from chewing on your tongue to a serious health condition like cancer. Some types of white spots on the tongue may appear more frequently in people who are immunocompromised.
Here are six possible causes for white spots on your tongue and how to treat them.
1. Trauma
If you have teeth with particularly sharp edges, or if you have a habit of chewing the sides of your tongue, this can cause the tissue to grow a thicker protective layer, sort of like a callus on your foot, says Felipe Nor, DDS, PhD, clinical assistant professor of oral medicine at the University of Michigan School of Dentistry.
Typically, these spots won't hurt, but if the trauma is more intense and acute, like if you bit down hard on your tongue, an ulcer may form, which can be very painful, says Nor.
Treatment: If you're chronically getting white spots due to trauma, the solution is to prevent the injuries to the tongue in the first place. Nor says this may include:
- Seeing your dentist to smooth down sharp teeth
- Stopping the habit of chewing on your tongue
- Wearing night guards or something similar if you are involuntarily chewing
2. Candidiasis (thrush)
Candidiasis, aka thrush, is an infection that leads to an overgrowth of yeast, a type of fungus, in your mouth, says Nor.
It is common in people who smoke or have dry mouth and causes small white spots, no more than a centimeter wide, to appear on the main surface of the tongue, where the taste buds are.
People who are immunocompromised are also at a higher risk for developing candidiasis, which may appear as larger spots anywhere on the tongue or inside the mouth. In particular, you might be most at risk if you have a condition like:
- HIV/AIDS
- Cancer
Aside from white patches on the tongue, other symptoms of oral thrush include:
- Soreness
- Redness
- Reduced taste
- Cottony sensation in the mouth
Treatment: You will need prescription antifungal medications from your doctor to stop the overgrowth of fungus, Nor says. These may include mouthwash or lozenges which work locally in the mouth, or in more severe cases, antifungal pills that work systemically.
3. Geographic tongue
Geographic tongue is an inflammatory condition of the tongue that results in white and red patches which may have slightly raised borders that quickly change shape and position every few hours.
The phenomenon appears like a geographic map, hence the name geographic tongue, says Gary Cash, DDS, board-certified dentist in private practice.
The exact cause of this condition is unknown, but there may be a genetic component, since some people with geographic tongue have a family history of it. Those who have a fissured tongue (deep grooves on its surface) may be more likely to have geographic tongue, as well.
Although the appearance of geographic tongue can be a little scary, it isn't harmful or contagious, Cash says.
In fact, many people with geographic tongue don't have symptoms aside from the tell-tale appearance, however, you might experience pain or burning when eating, particularly if consuming spicy or acidic foods. This is more intense than the type of "heat" or "burning" the average person might experience when having something spicy.
Treatment: There's no treatment for geographic tongue, but if you're experiencing pain, your dentist may recommend remedies such as over the counter pain relievers or mouthwashes that numb the area and/or reduce inflammation.
While the episodes will subside, people with the condition will have recurrences throughout their life, says Cash
4. Lichen planus
Oral lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that occurs when the immune system attacks cells in the mucous membranes of the mouth. If you have oral lichen planus, you might notice "lace-like" white patches on the tongue or on the inside of the cheeks, says Nor.
This condition is most common in middle-aged women and people who are immunocompromised. The cause is not completely known, but some triggers may include:
- Medications
- Infections
- Allergens
- Injuries to the mouth
- Stress
Aside from lacy-looking white patches, you may also have symptoms such as:
- Red and swollen patches
- Sores
These patches and sores can occur anywhere in the mouth, including:
- The tongue
- The inside of the cheeks
- The gums
- The inside of the cheeks
- The roof of the mouth
Treatment: A diagnosis typically requires a biopsy or culture to determine if there are any coccuring infections.
If you are asymptomatic aside from the white patches, your doctor will typically educate you on the condition and conduct follow-ups over time to make sure the lesions remain asymptomatic with no significant changes in their clinical appearance, says Nor.
However, if you are experiencing pain or ulcers, you may be prescribed numbing agents, topical steroids, or oral corticosteroids.
5. Human papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can affect not only the genitals, but also the mouth and throat. This usually results from tongue kissing or giving oral sex to a person with the virus.
On the tongue, HPV may manifest as white cauliflower-like lesions, says Nor. These spots are typically white, elevated, and benign.
If you have white spots or lesions in your mouth due to HPV, there is a risk of transmitting the virus to others, so it's best to avoid tongue kissing and sexual activity to be on the safe side.
Treatment: While it's possible for a healthy person to clear HPV on their own within one to two years, the lesions typically require surgical removal, says Nor.
A biopsy of the lesion may also be done to confirm the diagnosis.
6. Pre-cancer or cancer
The most serious potential cause of white spots on the tongue are related to precancer or cancer.
One example is leukoplakia, which results in otherwise asymptomatic white patches that can be precancerous, says Nor. It affects around 2.6% of the global population, and up to 17.5% of people with leukoplakia will go on to develop squamous cell carcinoma.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of cancer found on the tongue, which may result in white spots, says Cash. Symptoms may include:
- A lesion that looks like an ulcer
- A lesion that bleeds easily
Oral cancer accounts for 3% of total cancer cases, and squamous cell carcinoma accounts for about 90% of them.
Treatment: Whether your doctor thinks the lesion is pre-cancer or cancer, a biopsy of the lesion is necessary to identify the cause and develop a treatment plan. From there, cancer treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Insider's takeaway
If you're noticing new white spots on your tongue, your best bet is to see your dentist or doctor to get a diagnosis and have a proper course of treatment.
Whether the cause is something as simple as chewing on your tongue or a more serious health condition, a medical professional can help figure out what's going on and perform any biposies or samples to ensure your safety and health.